Cardiac shockwave therapy (CSWT) — a new non-invasive method for the treatment of coronary heart disease (CHD), whose mechanism of action is to stimulate the formation of new vessels in the myocardial ischemia zone, and allows patients to be treated in situations where traditional surgical approaches (coronary bypass, endovascular stenting, etc.) are impossible.
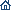
CSWT is carried out with the help of the world’s first high-performance shock wave therapy device for angina pectoris (coronary heart disease), especially in its hard to treat form.
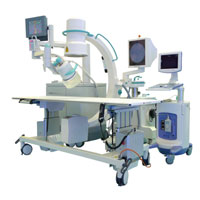
Precisely metered impact of low-energy shock wave impulses on the ischemic zones of the cardiac muscle stimulates the formation of new capillaries, enhances blood circulation and improves metabolism. The shock wave is guided by an ultrasound scanner with a cardiac sensor.
The effect of CSWT can be characterized as significant and prolonged. Several thousand shock waves are radiated to the ischemic region under continuous control of the built-in ultrasound in real time.
As a result, there has been a significant reduction in the number of complaints about traditional symptoms of angina and general improvement in cardiac function and metabolism. The procedure is performed without anesthesia and any sensation of pain in the patient, has no side effects.
Improvement of clinical and functional parameters is explained by reliable improvement of blood supply to the myocardium and a decrease in the number of ischemic areas.
Especially significant is the decrease in the number of nitroglycerin tablets taken. When taking computer tomography data, improvement of myocardial perfusion was observed in more than 60% of patients.
The main indications to the method:
- Impossibility of traditional surgical treatment of ischemic heart disease
- Stable exertional angina
- Cardiac Syndrome X
- The presence of myocardial segments with reversible ischemia
Noninvasive method of treatment of coronary heart disease (CHD), which allows to treat patients in situations when traditional surgical approaches (coronary bypass, endovascular stenting, etc.) are impossible.